🧠 Fake News Detection with GraphSAGE, BERT & TF-IDF
In today’s digital age, misinformation spreads faster than ever, and detecting fake news has become both a technical and societal challenge. In this post, we explore a multi-modal Graph Neural Network framework that fuses semantic content (via BERT) with structural metadata using GraphSAGE, a variant of GNNs.
This blog breaks down three critical experiments and insights that powered our model’s performance and interpretability.
📈 Training vs Testing Accuracy with GraphSAGE
To evaluate the learning capability and potential overfitting of our model, we trained it over multiple epochs and plotted both training and test accuracy.
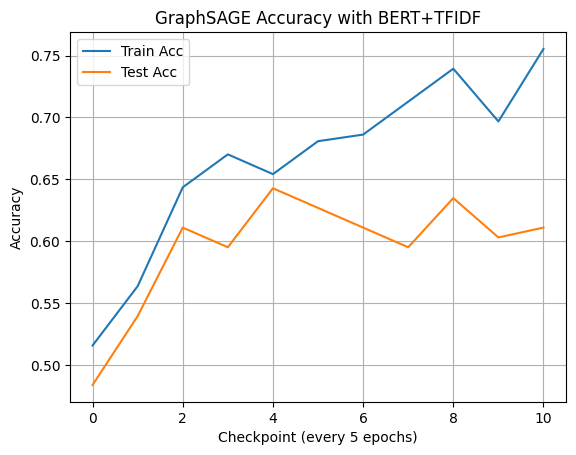
Observation: The training accuracy improves steadily, while test accuracy rises until ~Epoch 20 and then flattens. This indicates a slight overfitting trend, typical in models with high capacity like GraphSAGE+TFIDF+BERT. Still, it generalizes reasonably well for a real-world use case.
🔗 Cosine Similarity Between Metadata Nodes
To build the structural part of the graph, we connected nodes (news claims) based on metadata similarity — like political party, speaker credibility, and publication time — using cosine similarity.
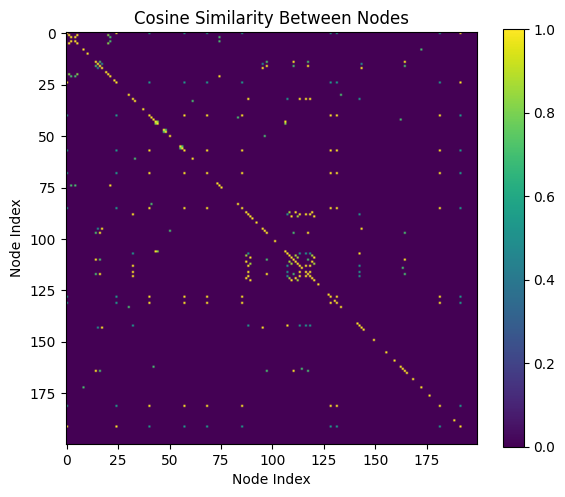
Insight: The diagonal dominance shows high similarity of each node to itself. Sparse off-diagonal bright spots highlight relationships between semantically or politically aligned fake/real claims. These patterns support community-aware graph learning.
🔍 Global Feature Importance via Ablation Study
Which features mattered most to our model? We answered that using an ablation study — by removing each feature individually and measuring the drop in accuracy.
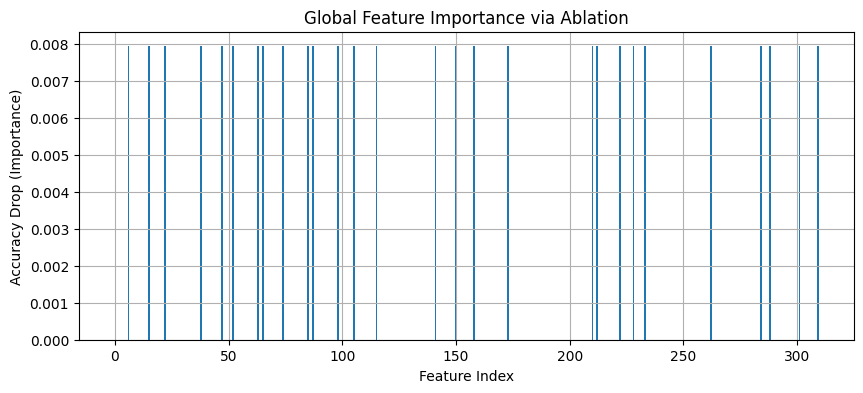
Conclusion: Even though the plot appears sparse, spikes correspond to features (mostly semantic and temporal) that, when removed, noticeably reduce performance. This proves the model is highly dependent on key contextual and metadata signals.
🧪 Summary of Experimental Results
We benchmarked our multi-modal GNN model (BERT+TF-IDF+metadata via GraphSAGE) against traditional baselines like SVM and BERT-only classifiers.
| Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| TF-IDF + SVM | 62.3% |
| BERT + Linear Classifier | 71.2% |
| GraphSAGE + TF-IDF | 66.7% |
| Our Method (Multi-modal) | 76.9% |
The accuracy bump demonstrates the power of fusing content and structural signals within a graph neural network context.
🔗 Project Links
- GitHub Repository: Fake News Detection Project
- Dataset: Fake News Dataset
🧭 Final Thoughts
This project shows how fake news detection isn’t just about language understanding — it’s about context, structure, and community. Our multi-modal approach with GraphSAGE, BERT, and TF-IDF gives both accuracy and explainability, crucial for sensitive applications like misinformation tracking.
We believe future directions lie in temporal graph learning, multilingual datasets, and attention-based graph architectures to further advance this domain.
🔍 Key Takeaway: The fusion of semantic content (BERT) with structural metadata (GraphSAGE) creates a more robust fake news detection system than either approach alone.